FSB_Rookie
New member
I acquired a 1996 full size bronco 2 years ago with 136k miles. It was in very good condition considering we are in the northeast. Within 3 weeks after I got it I had to replace the EGR valve. Now with 163k miles I have trouble codes P0401 and P0411. I have been driving and resetting, driving and resetting, driving and resetting waiting for the snow to finally melt to tackle this problem. Well today is the day. I read all the available postings I could find on these two trouble codes.
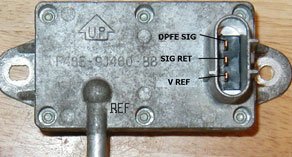
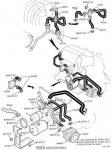
I check all the vacuum lines I could reach. Aside from one that is questionable, but tested as intact, I can't find any vacuum leaks. I tested the EGR valve with vacuum pump and it does not move at any level of vacuum pulled. I have a new one ordered and I will hopefully replace that tomorrow.
My question is: Can the malfunctioning EGR cause or create any conditions that would trigger the P0411 Secondary Air injection incorrect? Do I have two separate problems?
I need to get this fixed soon as my inspection has expired and it will not pass the emissions inspection. The Highway Patrol does not have the same libertarian view of emissions inspections that I do and I can only drive the back roads for so long!
Thanks for your assistance.
I check all the vacuum lines I could reach. Aside from one that is questionable, but tested as intact, I can't find any vacuum leaks. I tested the EGR valve with vacuum pump and it does not move at any level of vacuum pulled. I have a new one ordered and I will hopefully replace that tomorrow.
My question is: Can the malfunctioning EGR cause or create any conditions that would trigger the P0411 Secondary Air injection incorrect? Do I have two separate problems?
I need to get this fixed soon as my inspection has expired and it will not pass the emissions inspection. The Highway Patrol does not have the same libertarian view of emissions inspections that I do and I can only drive the back roads for so long!
Thanks for your assistance.